SCEA128 April 2023 LSF0102 , SN74AXC4T774 , SN74LXC1T45 , SN74LXC2T45 , SN74LXC8T245 , TXB0104 , TXS0102 , TXU0101 , TXU0102 , TXU0304
- 1
- Translate Voltages for SPI
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for UART
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for I2C
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for GPIO
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for SDIO
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for RGMII
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for MDIO
- Design Considerations
- Recommended Parts
- Translate Voltages for a SIM Card
- Design Considerations
- 25
The ability to apply machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms at the edge of computing and electronic system environments is more important today than ever before. Processing videos, images, audio, and other sensor data and then acting on that data at the edge enables higher performance more resilient systems. Bringing processing to the edge is enabling applications to take advantage of technologies such as real-time machine vision, audio transcription, video analytics and many others. One key enabling technology for bringing processing to the edge are System on Modules (SoMs) or Computer of Module (CoMs) Industrial Personal Computers (IPC). SoMs and CoMs are part of a broader category of computing platforms known as single board computers. Systems designers can leverage SoM and CoM modules to implement high performance embedded computing solutions. SoMs are essentially entire computer systems that are built in credit card sized or smaller form factor modules. The small size and low power dissipation of SoMs enables systems designers to bring processing power closer to the edge without having to sacrifice system form factors, processing density, or power budgets. SoMs are extremely popular within industrial applications spaces given the wide selection of SoM and CoM module offerings the market provides. What makes SoMs and CoMs especially versatile is the wide array of system interfaces that are supported by them. The large assortment of I/O (Input/Output) interface types enables SoMs to communicate with many different types of external peripheral devices that are likely to be used in an end application (see Figure 1).
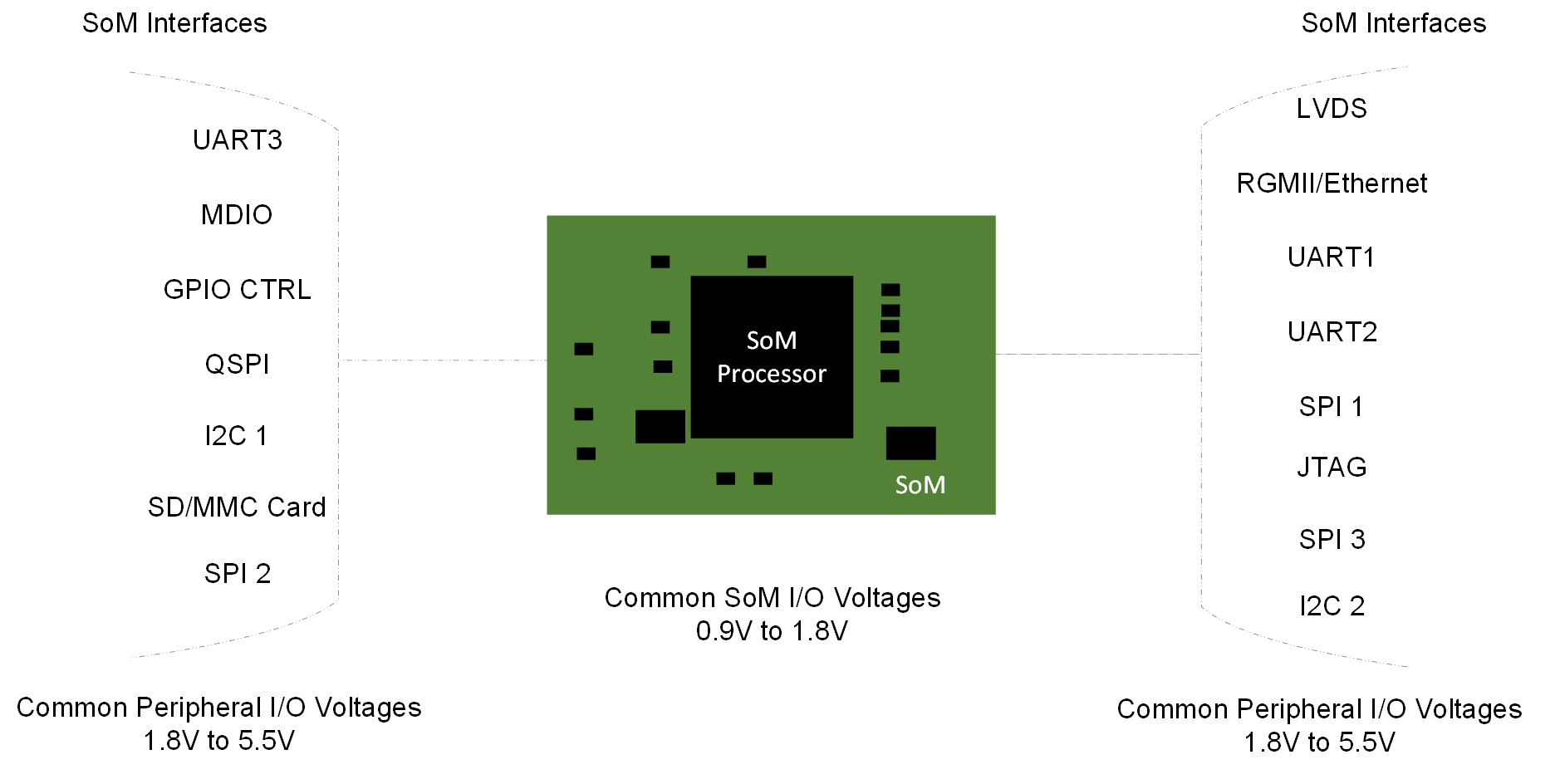 Figure 1 Common SoM and Industrial PC
I/O Interfaces
Figure 1 Common SoM and Industrial PC
I/O InterfacesAs the core processor devices that make up the SoM move down the silicon process curve, their core voltages also scale downward in order keep power dissipation reasonable while keeping heat dissipation manageable. The lower core voltages of SoM components also limits the I/O voltage that the SoM interfaces can operate at. The lower I/O voltages of new SoMs and CoMs presents a design challenge to design engineers who often need to interface these modules with peripheral devices operating at higher I/O voltages. One solution that system designers can use to resolve I/O level mismatches between SoM and peripheral device I/Os is to use I/O level shifter devices. Integrated I/O level translation solutions are available in a wide assortment of I/O types, bit widths, data rate ranges, current drive capabilities, and package options. Figure 1 shows common interfaces that are supported by mainstream SoMs while Table 1 shows recommended level translation solutions for level shifting between the different SoM and peripheral device I/O types. Texas Instruments’ portfolio of level shifter devices contains many different types of level translation functions that collectively is able to address almost any application requirement. TI’s level translation portfolio includes Auto Directional, Direction Controlled, and Fixed Direction level translators in Industrial, Automotive and Enhanced ratings. The sections below provide level translation recommendations for the most common interface types such as SPI, I2C, and UART. For more information on TI’s level translation devices, see the level translation landing page on ti.com.
| Interface | Translation Level | Small Package Option | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 3.6 V | Up to 5.5 V | ||
| FET Replacement | 2N7001T | SN74LXC1T45 / TXU0101 | DPW, DTQ |
| 1 Bit GPIO/Clock Signal | SN74AXC1T45 | SN74LXC1T45 / TXU0101 | DTQ |
| 2 Bit GPIO | SN74AXC2T245 | SN74LXC2T45 / TXU0102 | DTM |
| 2-Pin JTAG/UART | SN74AXC2T45 | SN74LXC2T45 / TXU0202 | DTM |
| I2C/MDIO/SMBus | TXS0102 / LSF0102 | TXS0102 / LSF0102 | DQE, DQM |
| IC-USB | SN74AVC2T872 / TXS0202 | NA | YZP |
| 4 Bit GPIO | SN74AXC4T245 | TXB0104 / TXU0104 | BQB, DTR |
| UART | SN74AXC4T245 | TXB0104 / TXU0204 | BQB, DTR |
| SPI | SN74AXC4T774 / TXB0104 | TXB0104 / TXU0304 | BQB, RUT |
| JTAG | SN74AXC4T774 / TXB0104 | TXB0104 / TXU0304 | BQB, RUT |
| I2S/PCM | SN74AXC4T774 / TXB0104 | TXB0104 / TXU0204 | BQB, RUT |
| Quad-SPI | TXB0106 | TXB0106 | RGY |
| SDIO/SD/MMC | TXS0206 / TWL1200 | NA | YFP |
| 8 Bit GPIO/RGMII | SN74AXC8T245 | SN74LXC8T245 | RJW, RHL |