SWRS108B May 2011 – June 2014 CC113L
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 Handling Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 General Characteristics
- 4.5 Current Consumption
- 4.6 RF Receive Section
- 4.7 Crystal Oscillator
- 4.8 Frequency Synthesizer Characteristics
- 4.9 DC Characteristics
- 4.10 Power-On Reset
- 4.11 Thermal Characteristics
- 4.12 Typical Characteristics
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Configuration Overview
- 5.4 Configuration Software
- 5.5 4-wire Serial Configuration and Data Interface
- 5.6 Microcontroller Interface and Pin Configuration
- 5.7 Data Rate Programming
- 5.8 Receiver Channel Filter Bandwidth
- 5.9 Demodulator, Symbol Synchronizer, and Data Decision
- 5.10 Packet Handling Hardware Support
- 5.11 Modulation Formats
- 5.12 Received Signal Qualifiers and RSSI
- 5.13 Radio Control
- 5.14 RX FIFO
- 5.15 Frequency Programming
- 5.16 VCO
- 5.17 Voltage Regulators
- 5.18 General Purpose and Test Output Control Pins
- 5.19 Asynchronous and Synchronous Serial Operation
- 5.20 System Consideration and Guidelines
- 5.21 Configuration Registers
- 5.22 Development Kit Ordering Information
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
- RF Performance
- Receive Sensitivity Down to −116 dBm at
0.6 kbps - Programmable Data Rate from 0.6 to 600 kbps
- Frequency Bands: 300–348 MHz,
387–464 MHz, and 779–928 MHz - 2-FSK, 4-FSK, GFSK, MSK, and OOK Supported
- Digital Features
- Flexible Support for Packet Oriented Systems
- On-chip Support for Sync Word Detection, Flexible Packet Length, and Automatic CRC Calculation
- Low-Power Features
- 200-nA Sleep Mode Current Consumption
- Fast Startup Time; 240 μs From Sleep to RX Mode
- 64-Byte RX FIFO
- General
- Few External Components; Completely On-chip Frequency Synthesizer, No External Filters or RF Switch Needed
- Green Package: RoHS Compliant and No Antimony or Bromine
- Small Size (QLP 4- x 4-mm Package, 20 Pins)
- Suited for Systems Targeting Compliance with EN 300 220 (Europe) and FCC CFR Part 15 (US)
- Support for Asynchronous and Synchronous Serial Transmit Mode for Backward Compatibility with Existing Radio Communication Protocols
1.2 Applications
- Ultra Low-Power Wireless Applications Operating in the 315-, 433-, 868-, 915-MHz ISM or SRD Bands
- Wireless Alarm and Security Systems
- Industrial Monitoring and Control
- Remote Controls
- Toys
- Home and Building Automation
1.3 Description
The CC113L is a cost optimized sub-1 GHz RF receiver for the 300–348 MHz, 387–464 MHz, and 779–928 MHz frequency bands. The circuit is based on the popular CC1101 RF transceiver, and RF performance characteristics are identical. The CC115L transmitter together with the CC113L receiver enable a low-cost RF link.
The RF receiver is integrated with a highly configurable baseband demodulator. The modem supports various modulation formats and has a configurable data rate up to 600 kbps.
The CC113L provides extensive hardware support for packet handling, data buffering, and burst transmissions.
The main operating parameters and the 64-byte receive FIFO of CC113L can be controlled through a serial peripheral interface (SPI). In a typical system, the CC113L will be used together with a microcontroller and a few additional passive components.
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows a functional block diagram of the device.
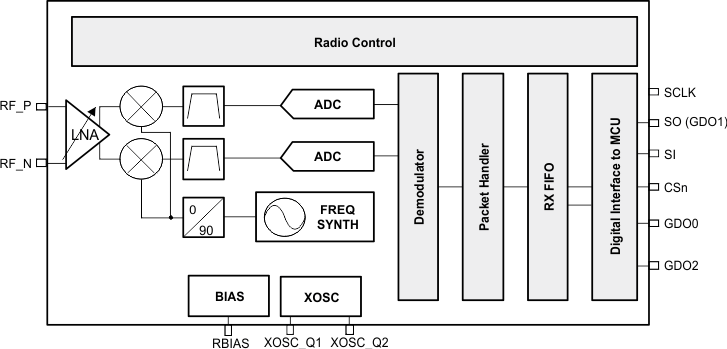 Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram