SPRS695D September 2011 – January 2016 AM3871 , AM3874
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1High-Performance System-on-Chip (SoC)
-
2Revision History
- 2.1 Device Comparison
- 2.2 Device Characteristics
- 2.3 Device Compatibility
- 2.4 ARM Cortex-A8 Microprocessor Unit (MPU) Subsystem Overview
- 2.5 Media Controller Overview
- 2.6 SGX530 Overview
- 2.7 Spinlock Module Overview
- 2.8 Mailbox Module Overview
- 2.9 Memory Map Summary
- 2.10 Pin Maps
- 2.11
Terminal Functions
- 2.11.1 Boot Configuration
- 2.11.2 Camera Interface (I/F)
- 2.11.3 Controller Area Network (DCAN) Modules (DCAN0, DCAN1)
- 2.11.4 DDR2/DDR3 Memory Controller
- 2.11.5 EDMA
- 2.11.6 EMAC [(R)(G)MII Modes] and MDIO
- 2.11.7 General-Purpose Input/Outputs (GPIOs)
- 2.11.8 GPMC
- 2.11.9 HDMI
- 2.11.10 I2C
- 2.11.11 McASP
- 2.11.12 McBSP
- 2.11.13 PCI-Express (PCIe)
- 2.11.14 Reset, Interrupts, and JTAG Interface
- 2.11.15 Serial ATA (SATA) Signals
- 2.11.16 SD Signals (MMC/SD/SDIO)
- 2.11.17 SPI
- 2.11.18 Oscillator/PLL, Audio Reference Clocks, and Clock Generator
- 2.11.19 Timer
- 2.11.20 UART
- 2.11.21 USB
- 2.11.22 Video Input (Digital)
- 2.11.23 Video Output (Digital)
- 2.11.24 Video Output (Analog, TV)
- 2.11.25 Reserved Pins
- 2.11.26 Supply Voltages
- 2.11.27 Ground Pins (VSS)
- 3Device Configurations
- 4 System Interconnect
- 5Device Operating Conditions
-
6Power, Reset, Clocking, and Interrupts
- 6.1 Power, Reset and Clock Management (PRCM) Module
- 6.2 Power
- 6.3
Reset
- 6.3.1 System-Level Reset Sources
- 6.3.2 Power-on Reset (POR pin)
- 6.3.3 External Warm Reset (RESET pin)
- 6.3.4 Emulation Warm Reset
- 6.3.5 Watchdog Reset
- 6.3.6 Software Global Cold Reset
- 6.3.7 Software Global Warm Reset
- 6.3.8 Test Reset (TRST pin)
- 6.3.9 Local Reset
- 6.3.10 Reset Priority
- 6.3.11 Reset Status Register
- 6.3.12 PCIE Reset Isolation
- 6.3.13 EMAC Switch Reset Isolation
- 6.3.14 RSTOUT_WD_OUT Pin
- 6.3.15 Effect of Reset on Emulation and Trace
- 6.3.16 Reset During Power Domain Switching
- 6.3.17 Pin Behaviors at Reset
- 6.3.18 Reset Electrical Data/Timing
- 6.4 Clocking
- 6.5 Interrupts
-
7 Peripheral Information and Timings
- 7.1 Parameter Information
- 7.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.3 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 7.4 EDMA
- 7.5 Emulation Features and Capability
- 7.6 Ethernet MAC Switch (EMAC SW)
- 7.7 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.8 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC) and Error Location Module (ELM)
- 7.9 High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 7.10 High-Definition Video Processing Subsystem (HDVPSS)
- 7.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.12 Imaging Subsystem (ISS)
- 7.13
DDR2/DDR3 Memory Controller
- 7.13.1 DDR2/3 Memory Controller Register Descriptions
- 7.13.2 DDR2/DDR3 PHY Register Descriptions
- 7.13.3 DDR-Related Control Module Registers Description
- 7.13.4
DDR2/DDR3 Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
- 7.13.4.1
DDR2 Routing Specifications
- 7.13.4.1.1
DDR2 Interface
- 7.13.4.1.1.1 DDR2 Interface Schematic
- 7.13.4.1.1.2 Compatible JEDEC DDR2 Devices
- 7.13.4.1.1.3 PCB Stackup
- 7.13.4.1.1.4 Placement
- 7.13.4.1.1.5 DDR2 Keepout Region
- 7.13.4.1.1.6 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.13.4.1.1.7 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.13.4.1.1.8 Net Classes
- 7.13.4.1.1.9 DDR2 Signal Termination
- 7.13.4.1.1.10 VREFSSTL_DDR Routing
- 7.13.4.1.2 DDR2 CK and ADDR_CTRL Routing
- 7.13.4.1.1
DDR2 Interface
- 7.13.4.2
DDR3 Routing Specifications
- 7.13.4.2.1 DDR3 versus DDR2
- 7.13.4.2.2 DDR3 EMIFs
- 7.13.4.2.3 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 7.13.4.2.4
DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 7.13.4.2.4.1 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 7.13.4.2.4.2 PCB Stackup
- 7.13.4.2.4.3 Placement
- 7.13.4.2.4.4 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 7.13.4.2.4.5 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.13.4.2.4.6 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.13.4.2.4.7 Net Classes
- 7.13.4.2.4.8 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 7.13.4.2.4.9 VREFSSTL_DDR Routing
- 7.13.4.2.4.10 VTT
- 7.13.4.2.4.11 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.13.4.2.4.12 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.13.4.2.4.13 Routing Specification
- 7.13.4.1
DDR2 Routing Specifications
- 7.14 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 7.15 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 7.16 MultiMedia Card/Secure Digital/Secure Digital Input Output (MMC/SD/SDIO)
- 7.17 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 7.18 Serial ATA Controller (SATA)
- 7.19 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 7.20 Timers
- 7.21 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 7.22 Universal Serial Bus (USB2.0)
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- CYE|684
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 High-Performance System-on-Chip (SoC)
1.1 Features
- High-Performance Sitara™ ARM® Processors
- ARM Cortex®-A8 Core
- ARMv7 Architecture
- In-Order, Dual-Issue, Superscalar Processor Core
- Neon™ Multimedia Architecture
- Supports Integer and Floating Point
- Jazelle® RCT Execution Environment
- ARMv7 Architecture
- ARM Cortex-A8 Memory Architecture
- 32KB of Instruction and Data Caches
- 512KB of L2 Cache
- 64KB of RAM, 48KB of Boot ROM
- 128KB of On-Chip Memory Controller (OCMC) RAM
- Imaging Subsystem (ISS)
- Camera Sensor Connection
- Parallel Connection for Raw (up to 16-Bit) and BT.656 or BT.1120 (8- and 16-Bit)
- Image Sensor Interface (ISIF) for Handling Image and Video Data From the Camera Sensor
- Resizer
- Resizing Image and Video From 1/16x to 8x
- Generating Two Different Resizing Outputs Concurrently
- Camera Sensor Connection
- Media Controller
- Controls the HDVPSS and ISS
- SGX530 3D Graphics Engine
- Delivers up to 25 MPoly/sec
- Universal Scalable Shader Engine (USSE™)
- Direct3D™ Mobile, OpenGLES 1.1 and 2.0, OpenVG™ 1.0, OpenMax™ API Support
- Advanced Geometry DMA-Driven Operation
- Programmable HQ Image Anti-Aliasing
- Endianness
- ARM Instructions and Data – Little Endian
- HD Video Processing Subsystem (HDVPSS)
- Two 165-MHz, 2-channel HD Video Capture Modules
- One 16- or 24-Bit Input or Dual 8-Bit SD Input Channels
- One 8-, 16-, or 24-Bit Input and One 8-Bit Only Input Channels
-
Two 165-MHz HD Video Display Outputs
- One 16-, 24-, or 30-Bit Output and One 16- or 24-Bit Output
- Composite or S-Video Analog Output
- Macrovision® Support Available
- Digital HDMI 1.3 Transmitter With Integrated PHY
- Advanced Video Processing Features Such as Scan, Format, Rate Conversion
- Three Graphics Layers and Compositors
- Two 165-MHz, 2-channel HD Video Capture Modules
-
Dual 32-Bit DDR2/DDR3 SDRAM Interfaces
- Supports up to DDR2-800 and DDR3-1066
- Up to Eight x 8 Devices Comprise 2GB of the Total Address Space
- Dynamic Memory Manager (DMM)
- Programmable Multizone Memory Mapping and Interleaving
- Enables Efficient 2D Block Accesses
- Supports Tiled Objects in 0°, 90°, 180°, or 270° Orientation and Mirroring
- Optimizes Interlaced Accesses
- General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 8- or 16-Bit Multiplexed Address and Data Bus
- 512MB of Address Space Divided Among up to 8 Chip Selects
- Glueless Interface to NOR Flash, NAND Flash (BCH/Hamming Error Code Detection), SRAM and Pseudo-SRAM
- Error Locator Module (ELM) Outside of GPMC to Provide up to 16-Bit or 512-Byte Hardware ECC for NAND
- Flexible Asynchronous Protocol Control for Interface to FPGA, CPLD, ASICs, and so Forth
- Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller
- Four Transfer Controllers
- 64 Independent DMA Channels and 8 Independent QDMA Channels
-
Dual-Port Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) With Optional Switch
- IEEE 802.3 Compliant (3.3-V I/O Only)
- MII/RMII/GMII/RGMII Media Independent Interfaces
- Management Data I/O (MDIO) Module
- Reset Isolation
- IEEE 1588 Time-Stamping and Industrial Ethernet Protocols
- Dual USB 2.0 Ports With Integrated PHYs
- USB2.0 High- and Full-Speed Clients
- USB2.0 High-, Full-, and Low-Speed Hosts, or OTG
- Supports End-point 0–15
- One PCI-Express® 2.0 Port With Integrated PHY
- Single Port With One Lane at 5.0 GT/s
- Configurable as Root Complex or End-point
- Eight 32-Bit General-Purpose Timers (Timer1–Timer8)
- One System Watchdog Timer (WDT0)
-
Six Configurable UART/IrDA/CIR Modules
- UART0 With Modem Control Signals
- Supports up to 3.6864 Mbps UART0/1/2
- Supports up to 12 Mbps UART3/4/5
- SIR, MIR, FIR (4.0 MBAUD), and CIR
-
Four Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPIs) (up to
48 MHz)- Each With Four Chip Selects
- Three MMC/SD/SDIO Serial Interfaces (up to
48 MHz)- Three Supporting up to 1-, 4-, or 8-Bit Modes
- Dual Controller Area Network (DCAN) Modules
- CAN Version 2 Part A, B
- Four Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C Bus) Ports
-
Six Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASPs)
- Dual 10 Serializer Transmit and Receive Ports
- Quad Four Serializer Transmit and Receive Ports
- DIT-Capable For S/PDIF (All Ports)
- Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- Transmit and Receive Clocks up to 48 MHz
- Two Clock Zones and Two Serial Data Pins
- Supports TDM, I2S, and Similar Formats
- Serial ATA (SATA) 3.0 Gbps Controller With Integrated PHY
- Direct Interface to One Hard Disk Drive
- Hardware-Assisted Native Command Queuing (NCQ) from up to 32 Entries
- Supports Port Multiplier and Command-Based Switching
- Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- One-Time or Periodic Interrupt Generation
- Up to 128 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) Pins
- One Spin Lock Module With up to 128 Hardware Semaphores
- One Mailbox Module With 12 Mailboxes
- On-Chip ARM ROM Bootloader (RBL)
- Power, Reset, and Clock Management
- Multiple Independent Core Power Domains
- Multiple Independent Core Voltage Domains
- Support for Three Operating Points (OPP100, OPP120, OPP166) per Voltage Domain
- Clock Enable and Disable Control for Subsystems and Peripherals
- 32KB of Embedded Trace Buffer (ETB) and
5-Pin Trace Interface for Debug - IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Compatible
- 684-Pin Pb-Free BGA Package (CYE Suffix),
0.8-mm Ball Pitch With Via Channel Technology to Reduce PCB Cost - 45-nm CMOS Technology
- 1.8- and 3.3-V Dual Voltage Buffers for General I/O
1.2 Applications
- Single-Board Computing
- Network and Communications Processing
- Industrial Automation
- Human Machine Interface
- Interactive Point-of-Service and Information Kiosks
- Portable Data Terminals
1.3 Description
AM387x Sitara ARM processors are highly integrated, programmable platforms that leverage the Sitara processor technology.
The device enables Original-Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original-Design Manufacturers (ODMs) to quickly bring to market devices featuring robust operating systems support, rich user interfaces, and high processing performance through the maximum flexibility of a fully integrated mixed processor solution. The device also combines programmable ARM processing with a highly integrated peripheral set.
The AM387x Sitara ARM processors also present OEMs and ODMs with new levels of processor scalability and software reuse. An OEM or ODM who used the AM387x processors in a design and can make a similar product with added features could scale up to the pin-compatible and software-compatible TMS320DM814x processors from TI. The TMS320DM814x DaVinci video processors add a powerful C674x core DSP along with a video encoder and decoder to the hardware on the AM387x. Additionally, OEMs or ODMs that have used the AM387x or DM814x processors and find a need for a faster ARM and/or DSP core performance could scale up to the software-compatible AM389x or TMS320DM816x devices with higher core speeds.
Programmability is provided by an ARM Cortex-A8 RISC CPU with Neon extension. The ARM processor lets developers keep control functions separate from algorithms programmed on coprocessors, thus reducing the complexity of the system software. The ARM Cortex-A8 32-bit RISC core with Neon floating-point extension includes: 32KB of instruction cache; 32KB of data cache; 512KB of L2 cache; 48KB of boot ROM; and 64KB of RAM.
The AM387x Sitara ARM processors also include an SGX530 3D graphics engine to off-load many graphics processing tasks from the ARM core, making more ARM MIPS available for common processing tasks on algorithms. Additionally, the AM387x processor has a complete set of development tools for the ARM which include C compilers and a Microsoft® Windows® debugger interface for visibility into source code execution.
Device Information
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE |
|---|---|---|
| AM3874 | CYE (684) | 23 mm × 23 mm |
| AM3871 | CYE (684) | 23 mm × 23 mm |
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows the functional block diagram of the device.
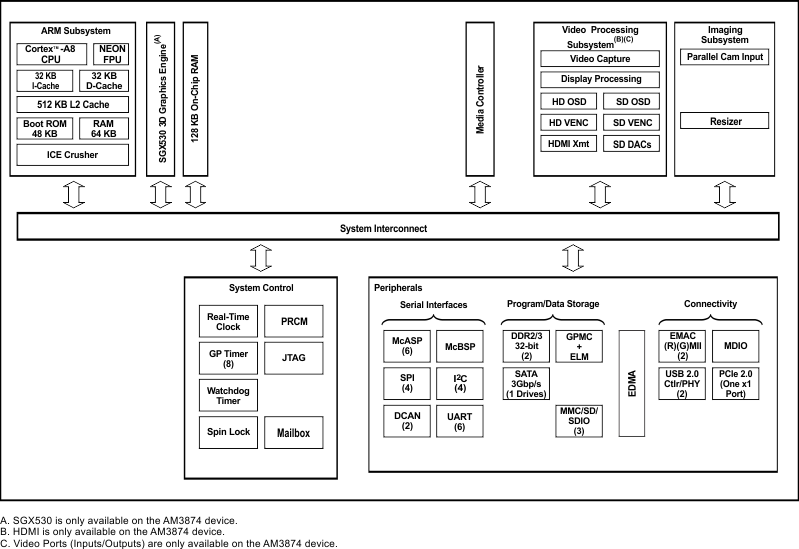 Figure 1-1 AM387x Sitara ARM Processors Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 AM387x Sitara ARM Processors Functional Block Diagram