SBAS668A May 2014 – June 2015 ADC32J22 , ADC32J23 , ADC32J24 , ADC32J25
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADC32J22, ADC32J23
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: ADC32J24, ADC32J25
- 7.8 AC Performance: ADC32J25
- 7.9 AC Performance: ADC32J24
- 7.10 AC Performance: ADC32J23
- 7.11 AC Performance: ADC32J22
- 7.12 Digital Characteristics
- 7.13 Timing Requirements
- 7.14 Typical Characteristics: ADC32J25
- 7.15 Typical Characteristics: ADC32J24
- 7.16 Typical Characteristics: ADC32J23
- 7.17 Typical Characteristics: ADC32J22
- 7.18 Typical Characteristics: Common Plots
- 7.19 Typical Characteristics: Contour Plots
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Summary of Special Mode Registers
- 9.6.2
Serial Register Descriptions
- 9.6.2.1 Register 01h (address = 01h)
- 9.6.2.2 Register 03h (address = 03h)
- 9.6.2.3 Register 04h (address = 04h)
- 9.6.2.4 Register 06h (address = 06h)
- 9.6.2.5 Register 07h (address = 07h)
- 9.6.2.6 Register 08h (address = 08h)
- 9.6.2.7 Register 09h (address = 09h)
- 9.6.2.8 Register 0Ah (address = 0Ah)
- 9.6.2.9 Register 0Bh (address = 0Bh)
- 9.6.2.10 Register 0Ch (address = 0Ch)
- 9.6.2.11 Register 0Dh (address = 0Dh)
- 9.6.2.12 Register 0Eh (address = 0Eh)
- 9.6.2.13 Register 0Fh (address = 0Fh)
- 9.6.2.14 Register 13h (address = 13h)
- 9.6.2.15 Register 15h (address = 15h)
- 9.6.2.16 Register 27h (address = 27h)
- 9.6.2.17 Register 2Ah (address = 2Ah)
- 9.6.2.18 Register 2Bh (address = 2Bh)
- 9.6.2.19 Register 2Fh (address = 2Fh)
- 9.6.2.20 Register 30h (address = 30h)
- 9.6.2.21 Register 31h (address = 31h)
- 9.6.2.22 Register 34h (address = 34h)
- 9.6.2.23 Register 3Ah (address = 3Ah)
- 9.6.2.24 Register 3Bh (address = 3Bh)
- 9.6.2.25 Register 3Ch (address = 3Ch)
- 9.6.2.26 Register 422h (address = 422h)
- 9.6.2.27 Register 434h (address = 434h)
- 9.6.2.28 Register 522h (address = 522h)
- 9.6.2.29 Register 534 (address = 534h)
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Orderable Information
1 Features
- Dual Channel
- 12-Bit Resolution
- Single 1.8-V Supply
- Flexible Input Clock Buffer with Divide-by-1, -2, -4
- SNR = 70.3 dBFS, SFDR = 88 dBc at
fIN = 70 MHz - Ultralow Power Consumption:
- 227 mW/Ch at 160 MSPS
- Channel Isolation: 105 dB
- Internal Dither
- JESD204B Serial Interface:
- Subclass 0, 1, 2 Compliant up to 3.2 Gbps
- Supports One Lane per ADC up to 160 MSPS
- Support for Multichip Synchronization
- Pin-to-Pin Compatible with 14-Bit Version (ADC32J4X)
- Package: VQFN-48 (7 mm × 7 mm)
2 Applications
- Multi-Carrier, Multi-Mode Cellular Base Stations
- Radar and Smart Antenna Arrays
- Munitions Guidance
- Motor Control Feedback
- Network and Vector Analyzers
- Communications Test Equipment
- Nondestructive Testing
- Microwave Receivers
- Software Defined Radios (SDRs)
- Quadrature and Diversity Radio Receivers
3 Description
The ADC32J2x is a high-linearity, ultra-low power, dual-channel, 12-bit, 50-MSPS to 160-MSPS, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) family. The devices are designed specifically to support demanding, high input frequency signals with large dynamic range requirements. A clock input divider allows more flexibility for system clock architecture design and the SYSREF input enables complete system synchronization. The devices support JESD204B interfaces in order to reduce the number of interface lines, thus allowing for high system integration density. The JESD204B interface is a serial interface, where the data of each ADC are serialized and output over only one differential pair. An internal phase-locked loop (PLL) multiplies the incoming ADC sampling clock by 20 to derive the bit clock that is used to serialize the 12-bit data from each channel. The devices support subclass 1 with interface speeds up to 3.2 Gbps.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| ADC32J2X | VQFN (48) | 7.00 mm × 7.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the package option addendum at the end of the datasheet.
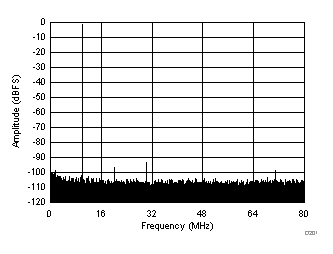
FFT with Dither On
(fS = 160 MSPS, SNR = 70.3 dBFS, fIN = 10 MHz, SFDR = 92.6 dBc)
4 Revision History
Changes from * Revision (May 2015) to A Revision
- Changed from product preview to production dataGo