SPRSP19 December 2017 TMS320F28377D-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.6 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.7
System
- 4.7.1 Power Sequencing
- 4.7.2 Reset Timing
- 4.7.3 Clock Specifications
- 4.7.4 Flash Parameters
- 4.7.5 Emulation/JTAG
- 4.7.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.7.7 Interrupts
- 4.7.8 Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.9 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 4.8 Analog Peripherals
- 4.9 Control Peripherals
- 4.10
Communications Peripherals
- 4.10.1 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 4.10.2 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 4.10.3 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.10.4 Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 4.10.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.10.6 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 4.10.7 Universal Parallel Port (uPP) Interface
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Memory
- 5.4 Identification
- 5.5 Bus Architecture - Peripheral Connectivity
- 5.6 C28x Processor
- 5.7 Control Law Accelerator
- 5.8 Direct Memory Access
- 5.9 Interprocessor Communication Module
- 5.10 Boot ROM and Peripheral Booting
- 5.11 Dual Code Security Module
- 5.12 Timers
- 5.13 Nonmaskable Interrupt With Watchdog Timer (NMIWD)
- 5.14 Watchdog
- 5.15 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PTP|176
Orderable Information
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
- Dual-Core Architecture
- Two TMS320C28x 32-Bit CPUs
- 200 MHz
- IEEE 754 Single-Precision Floating-Point Unit (FPU)
- Trigonometric Math Unit (TMU)
- Viterbi/Complex Math Unit (VCU-II)
- Two Programmable Control Law Accelerators (CLAs)
- 200 MHz
- IEEE 754 Single-Precision Floating-Point Instructions
- Executes Code Independently of Main CPU
- On-Chip Memory
- 512KB (256KW) or 1MB (512KW) of Flash (ECC-Protected)
- 172KB (86KW) or 204KB (102KW) of RAM (ECC-Protected or Parity-Protected)
- Dual-Zone Security Supporting Third-Party Development
- Clock and System Control
- Two Internal Zero-Pin 10-MHz Oscillators
- On-Chip Crystal Oscillator
- Windowed Watchdog Timer Module
- Missing Clock Detection Circuitry
- 1.2-V Core, 3.3-V I/O Design
- System Peripherals
- Two External Memory Interfaces (EMIFs) With ASRAM and SDRAM Support
- Dual 6-Channel Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controllers
- Up to 169 Individually Programmable, Multiplexed General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Pins With Input Filtering
- Expanded Peripheral Interrupt Controller (ePIE)
- Multiple Low-Power Mode (LPM) Support With External Wakeup
- Communications Peripherals
- USB 2.0 (MAC + PHY)
- Support for 12-Pin 3.3 V-Compatible Universal Parallel Port (uPP) Interface
- Two Controller Area Network (CAN) Modules (Pin-Bootable)
- Three High-Speed (up to 50-MHz) SPI Ports (Pin-Bootable)
- Two Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports (McBSPs)
- Four Serial Communications Interfaces (SCI/UART) (Pin-Bootable)
- Two I2C Interfaces (Pin-Bootable)
- Analog Subsystem
- Up to Four Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)
- 16-Bit Mode
- 1.1 MSPS Each (up to 4.4-MSPS System Throughput)
- Differential Inputs
- Up to 12 External Channels
- 12-Bit Mode
- 3.5 MSPS Each (up to 14-MSPS System Throughput)
- Single-Ended Inputs
- Up to 24 External Channels
- Single Sample-and-Hold (S/H) on Each ADC
- Hardware-Integrated Post-Processing of ADC Conversions
- Saturating Offset Calibration
- Error From Setpoint Calculation
- High, Low, and Zero-Crossing Compare, With Interrupt Capability
- Trigger-to-Sample Delay Capture
- 16-Bit Mode
- Eight Windowed Comparators With 12-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) References
- Three 12-Bit Buffered DAC Outputs
- Up to Four Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)
- Enhanced Control Peripherals
- 24 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Channels With Enhanced Features
- 16 High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM) Channels
- High Resolution on Both A and B Channels of 8 PWM Modules
- Dead-Band Support (on Both Standard and High Resolution)
- Six Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Modules
- Three Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP) Modules
- Eight Sigma-Delta Filter Module (SDFM) Input Channels, 2 Parallel Filters per Channel
- Standard SDFM Data Filtering
- Comparator Filter for Fast Action for Out of Range
- Package Options:
- 337-Ball New Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array (nFBGA) [GWT Suffix]
- 176-Pin PowerPAD™ Thermally Enhanced Low-Profile Quad Flatpack (HLQFP) [PTP Suffix]
-
Supports Defense, Aerospace, and Medical Applications:
- Controlled Baseline
- One Assembly/Test Site
- One Fabrication Site
- Available in Extended (–55°C to 125°C) Temperature Range
- Extended Product Life Cycle
- Extended Product-Change Notification
- Product Traceability
1.2 Applications
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- Building Automation
- Electronic Point of Sale
- Electric Vehicle/Hybrid Electric Vehicle (EV/HEV) Powertrain
- Factory Automation
- Grid Infrastructure
- Industrial Transport
- Medical, Healthcare and Fitness
- Motor Drives
- Power Delivery
- Telecom Infrastructure
- Test and Measurement
1.3 Description
The Delfino™ TMS320F28377D-EP is a powerful 32-bit floating-point microcontroller unit (MCU) designed for advanced closed-loop control applications such as industrial drives and servo motor control; solar inverters and converters; digital power; transportation; and power line communications. Complete development packages for digital power and industrial drives are available as part of the powerSUITE and DesignDRIVE initiatives. While the Delfino product line is not new to the TMS320C2000™ portfolio, the F28377D supports a new dual-core C28x architecture that significantly boosts system performance. The integrated analog and control peripherals also let designers consolidate control architectures and eliminate multiprocessor use in high-end systems.
The dual real-time control subsystems are based on TI’s 32-bit C28x floating-point CPUs, which provide 200 MHz of signal processing performance in each core. The C28x CPUs are further boosted by the new TMU accelerator, which enables fast execution of algorithms with trigonometric operations common in transforms and torque loop calculations; and the VCU accelerator, which reduces the time for complex math operations common in encoded applications.
The F28377D microcontroller features two CLA real-time control coprocessors. The CLA is an independent 32-bit floating-point processor that runs at the same speed as the main CPU. The CLA responds to peripheral triggers and executes code concurrently with the main C28x CPU. This parallel processing capability can effectively double the computational performance of a real-time control system. By using the CLA to service time-critical functions, the main C28x CPU is free to perform other tasks, such as communications and diagnostics. The dual C28x+CLA architecture enables intelligent partitioning between various system tasks. For example, one C28x+CLA core can be used to track speed and position, while the other C28x+CLA core can be used to control torque and current loops.
The TMS320F28377D-EP supports 1MB (512KW) of onboard flash memory with error correction code (ECC) and 204KB (102KW) of SRAM. Two 128-bit secure zones are also available on each CPU for code protection.
Performance analog and control peripherals are also integrated on the F28377D MCU to further enable system consolidation. Four independent 16-bit ADCs provide precise and efficient management of multiple analog signals, which ultimately boosts system throughput. The new sigma-delta filter module (SDFM) works in conjunction with the sigma-delta modulator to enable isolated current shunt measurements. The Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS) with windowed comparators allows for protection of power stages when current limit conditions are exceeded or not met. Other analog and control peripherals include DACs, PWMs, eCAPs, eQEPs, and other peripherals.
Peripherals such as EMIFs, CAN modules (ISO 11898-1/CAN 2.0B-compliant), and a new uPP interface extend the connectivity of the F28377D. The uPP interface is a new feature of the C2000™ MCUs and supports high-speed parallel connection to FPGAs or other processors with similar uPP interfaces. Lastly, a USB 2.0 port with MAC and PHY lets users easily add universal serial bus (USB) connectivity to their application.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE |
|---|---|---|
| TMS320F28377D-EP | nFBGA (337) | 16.0 mm × 16.0 mm |
| HLQFP (176) | 24.0 mm × 24.0 mm |
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows the CPU system and associated peripherals.
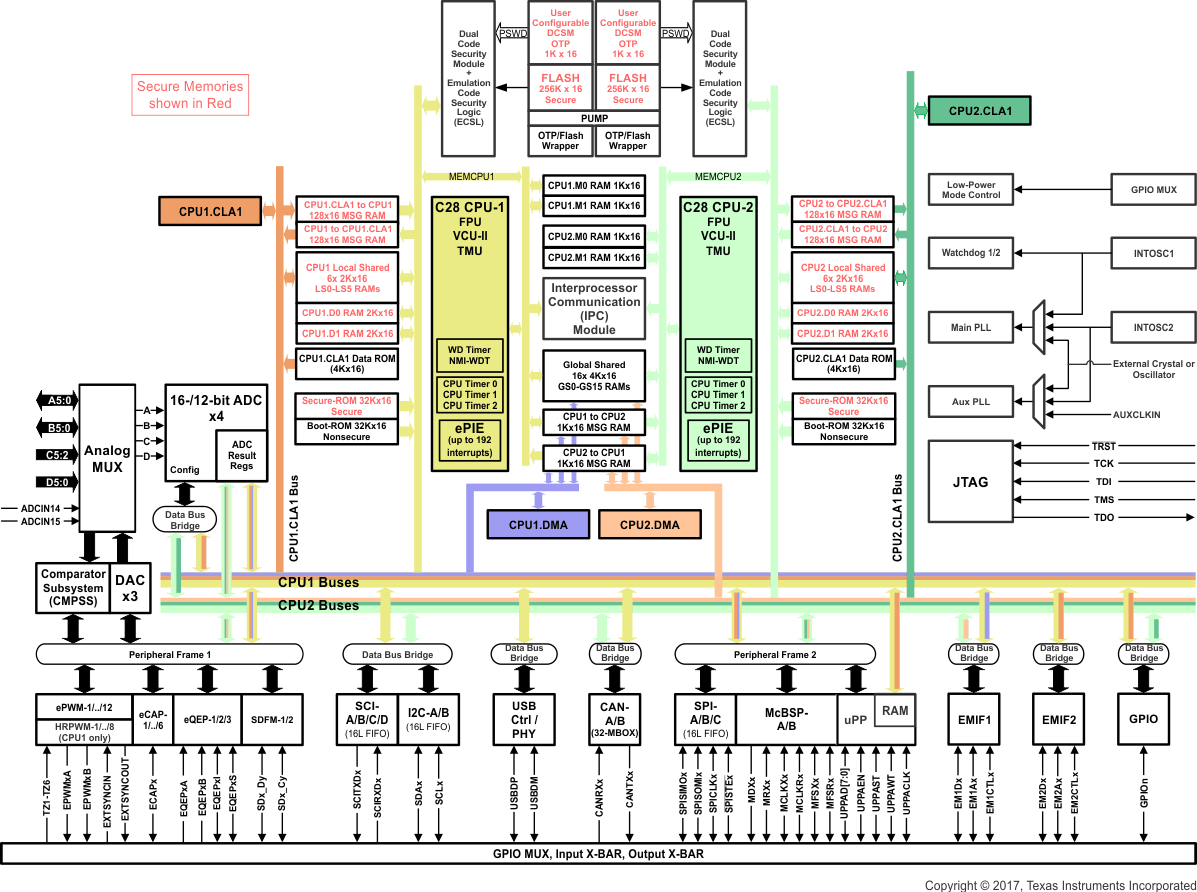 Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram